
Neptune, the Ray of Light for Romanian energy dependency
The Neptun Deep project is viewed as a pivotal opportunity for Romania's economy and energy independence.
A collection of 179 posts

The Neptun Deep project is viewed as a pivotal opportunity for Romania's economy and energy independence.
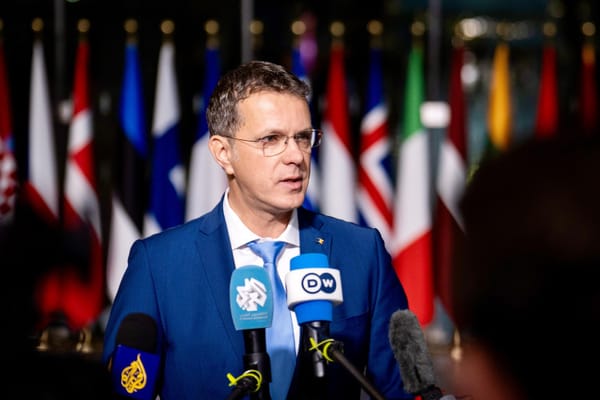

The minister highlighted by resigning he aimed to prevent further distractions from national security concerns.
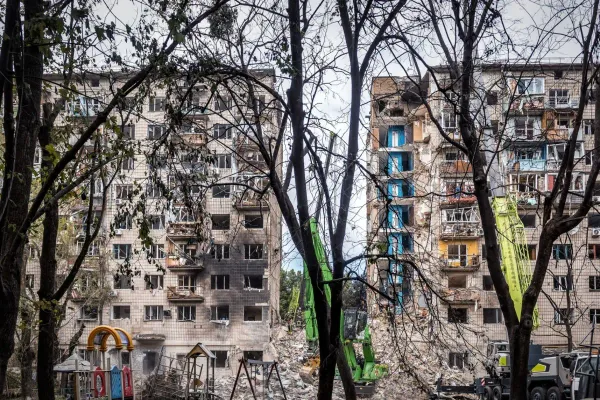

Public attitudes toward the war in Ukraine vary highly and have shifted significantly across the CEE region.
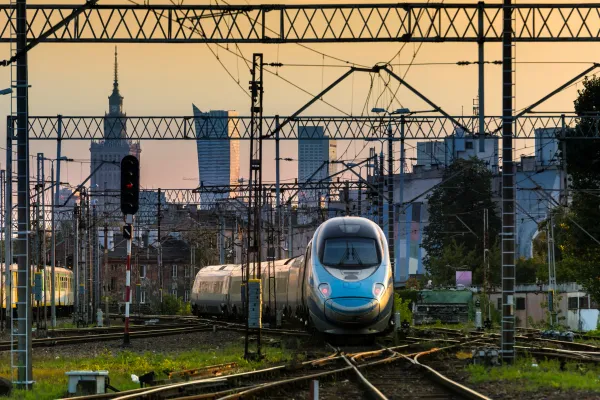

Polish police have made another arrest in connection with a serious railway sabotage case.

Croatia has concluded that the June 2023 Hungarian military helicopter crash was caused by human error after the crew deviated from its flight path.

CEE countries differ on euro adoption, some view it as a path to convergence, while others wary of potential negative effects.
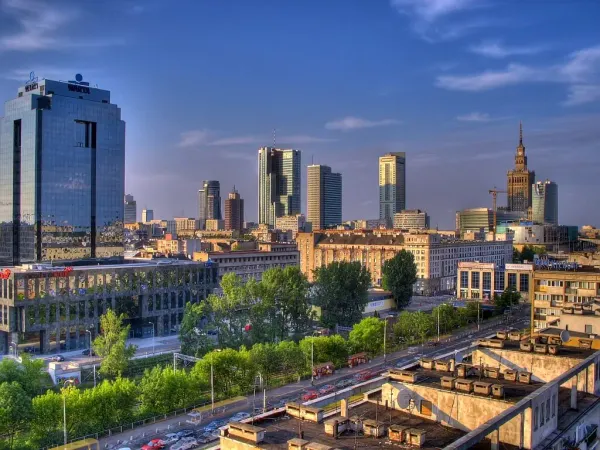

Poland’s economic weight is undoubtedly increasing in the region, with Polish-German economic relations and political tensions deepening.

Romania is projected to see modest growth and a gradual narrowing of the budget deficit over the next three years.

More and more migrants enter the EU via its northeast border, making Poland a buffer against Moscow’s politically driven bid to destabilize Europe.

Orbán’s White House visit secured Hungary’s US sanctions exemptions and imply the start of a golden era in bilateral ties.

Romanian and NATO leaders held talks focusing on strengthening Romania’s security amid ongoing regional tensions.
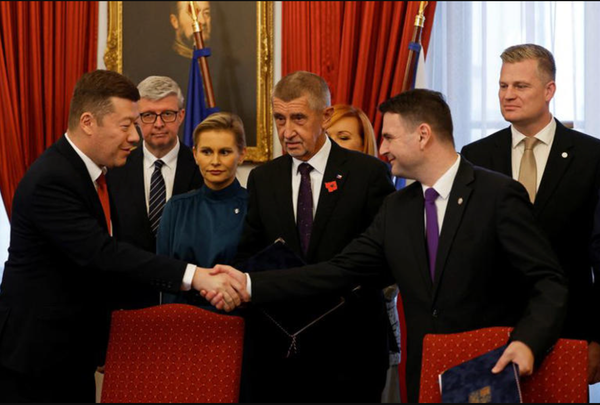

Andrej Babiš’s ANO movement returns to power in coalition with nationalist allies, promising social protection, lower energy prices, and a tougher stance toward Brussels.
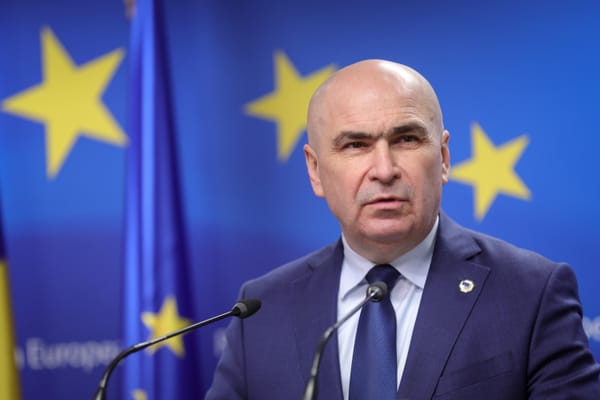

Romanian PM Ilie Bolojan warned that peace is no longer guaranteed, stressing that ensuring security is a shared responsibility of society.
As the EU tightens sanctions on Russia, Central European states display contrasting political stances rooted in their priorities and capacities.

The Central and Eastern European oil market is entering a new era as a result of the US measures aimed at restricting Russian crude exports.