Czechia, Hungary, Estonia top for employment in CEE - Eurostat report
Estonia had the highest employment rate in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) of 81.9% in 2022, according to the recently released data of the EU statistics agency Eurostat.
Just behind the Baltic country were Czechia, with 81.3%, and Hungary (80.2%). The middle grouping of the EU member states in CEE consisted of Lithuania (79%), Slovenia (77.9%), Austria (77.3%) and Latvia (77%).
Just behind were Poland and Slovakia (both on 76.7%) and Bulgaria (75.7%). The laggards for employment rates in CEE were Croatia, which had a rate of only 69.7%, slightly ahead of bottom-placed Romania, where the rate was 68.5% in 2022.
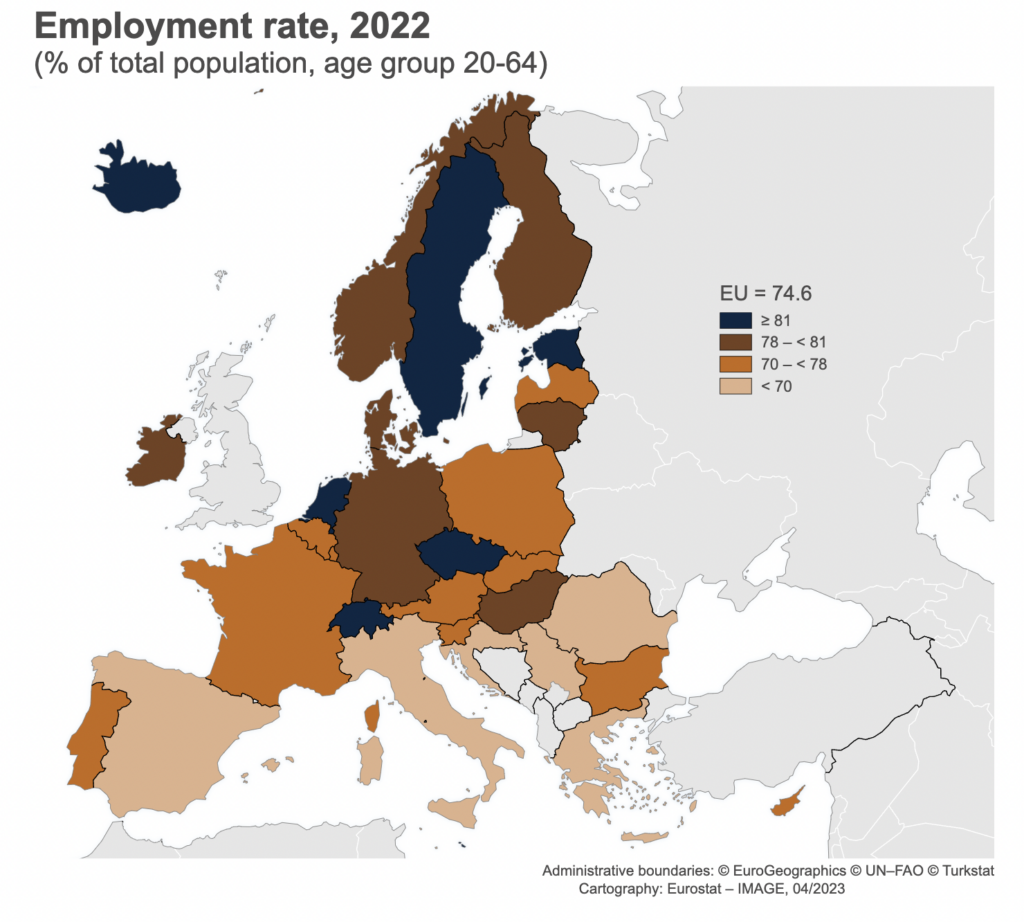
Among the EU countries as a whole, 11 had employment rates above 78% (one of the three targets set in the 2030 action plan of the EU’s European Pillar of Social Rights), with the Netherlands (83%), Sweden, and Estonia (both 82%) having the highest rates, Eurostat reported, adding that the lowest rates were recorded in Italy (65%) and Greece (66%).
Women more likely to be over-qualified than men
In 19 of the 27 EU countries, women had higher over-qualification rates than men, with the largest differences recorded in Malta (+11 pp), Cyprus (+8 pp), Italy, and Slovakia (both +7 pp). However, in eight EU countries, men had higher over-qualification rates, with the biggest differences recorded in Baltic countries: Lithuania (+5 pp), Estonia, and Latvia (each +4 pp).
In the EU, the over-qualification rate was highest in Spain (36%), followed by Greece and Cyprus (each 32%). Meanwhile, Luxembourg (7%), Sweden, Denmark, Hungary, and Czechia (each 14%) recorded the lowest rates.
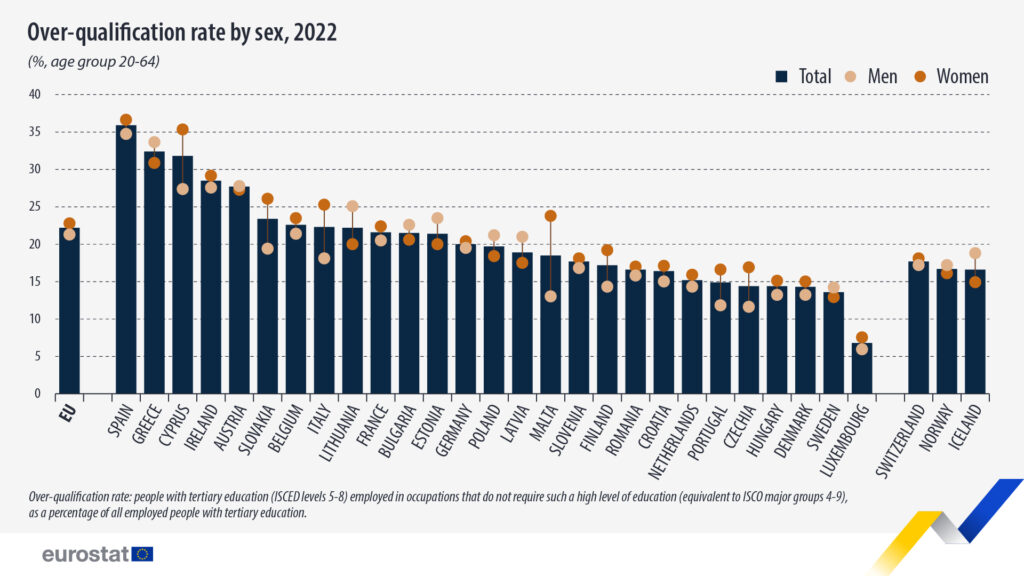
In 2022, the EU over-qualification rate was 22%, with 21% for men and 23% for women, according to Eurostat. Over-qualification is when people with tertiary education are employed in occupations that do not require such a high level of education, Eurostat wrote, adding that “since 2023 is the European Year of Skills, these statistics might help to inform policymakers how people in the EU fare in terms of application of their qualifications.”
When the 2023 European Year of Skills was launched, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said “We need much more focus in our investment on professional education and upskilling, we need better cooperation with companies, because they know best what they need, and we need to match these needs with people’s aspirations. But we also have to attract the right skills to our continent, skills that help companies and strengthen Europe’s growth,” von der Leyen added.